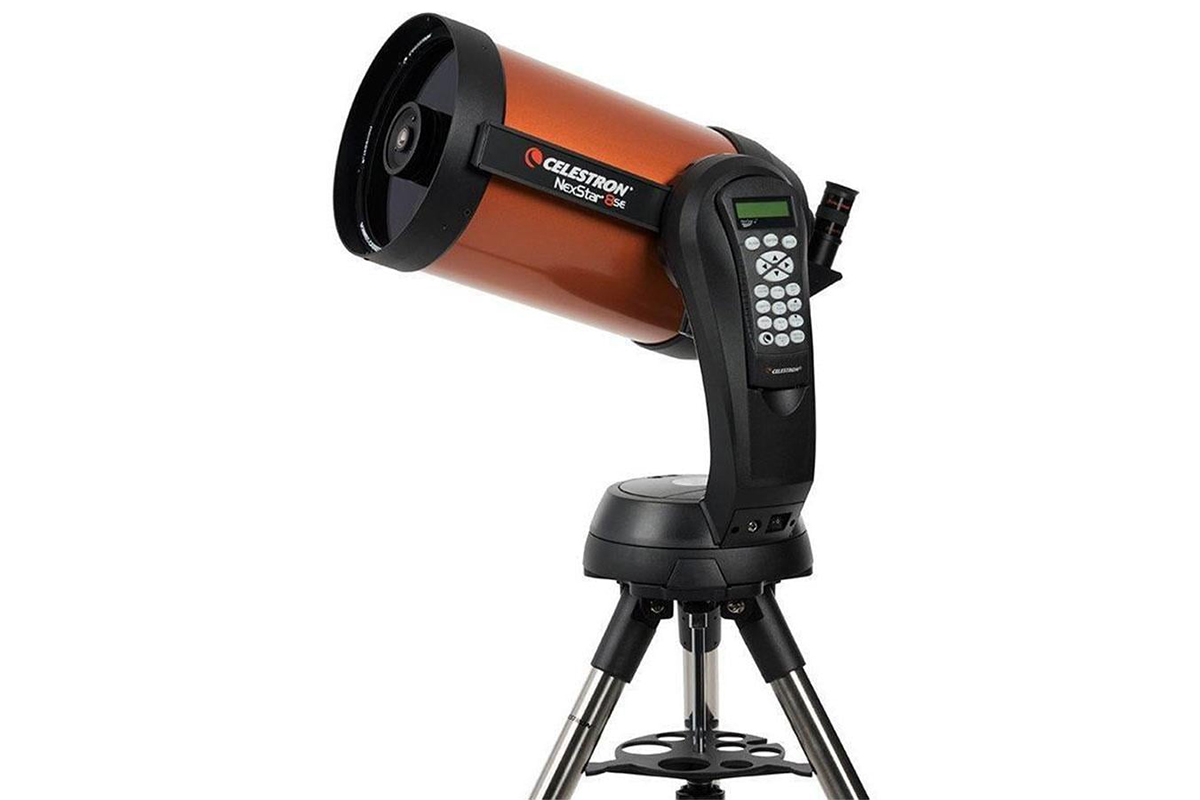
Reflecting telescope
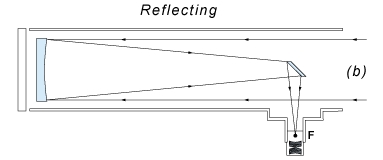 It is based on the use of mirrors to direct the light received, focus it and form the image. Reflecting telescopes are characterized by making the light beam that enters the tube hit twice, instead of only passing it once through a lens like refractors. First the light hits a primary parabolic (or spherical) mirror, located at the base of the tube, and then bounces to a secondary flat mirror, located shortly before the upper end, and finally the concentrated light will finally hit an eyepiece. The use of mirrors instead of lenses is a great advantage in optical astronomy, since the mirrors can be large without causing distortion in the images obtained, as happens with reflectors.
It is based on the use of mirrors to direct the light received, focus it and form the image. Reflecting telescopes are characterized by making the light beam that enters the tube hit twice, instead of only passing it once through a lens like refractors. First the light hits a primary parabolic (or spherical) mirror, located at the base of the tube, and then bounces to a secondary flat mirror, located shortly before the upper end, and finally the concentrated light will finally hit an eyepiece. The use of mirrors instead of lenses is a great advantage in optical astronomy, since the mirrors can be large without causing distortion in the images obtained, as happens with reflectors.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages – The apertures are very varied, without affecting too much the compactness and transportability of the telescope
– The apertures are very varied, without affecting too much the compactness and transportability of the telescope
– They are ideal for deep space objects
– They are more economical at large apertures, compared to refractors
– Eliminate chromatic aberration
– They operate in a broader spectrum of light, passing wavelengths that a refractor lens would absorb
– Its manufacturing cost is not too high and it is feasible to build one at home
Disadvantages
– Spherical aberration and coma may occur.
– When the tube is open, it is exposed to dust and humidity
– At short focal ratios, the size of the secondary mirror increases, decreasing the contrast and sharpness of the image
– The optical system is sensitive to misalignment if subjected to a strong impact
Reflectors solve some problems with refracting telescopes, but they often come with some minor image distortion problems. However, they are the most used by amateur astronomers, thanks to their high performance and the option of having more compact designs that are easy to transport to observation sites far from the city. Likewise, the materials that make up a reflecting telescope lead to an increase in price, although for large apertures, it is more convenient than a refractor.


