Cosmology corresponds to the study of the origin, structure and laws of the Universe as we know it, describing its nature. Its scope covers both the composition of the Universe, its expansion and laws that compose it, as well as the search for a theory that manages to unify physics and the 4 fundamental forces: weak nuclear interaction, strong nuclear interaction, gravity and electromagnetism.
Throughout history there have been 3 main theories to explain the origin of the Universe (although all of them have undergone modifications and adjustments), where the most accepted has been that of big Bang, and therefore what we seek to determine are the conditions that gave rise to said event.
Main theories of the beginning of the Universe
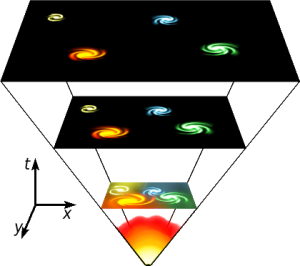
Big Bang Theory
It says that the Universe began from the explosion of a superhot and superdense atom (in a singularity), which in this way began to expand to the present day. This theory postulates the origin of the Universe about 13.7 billion years ago, and is supported by several proven evidence, such as the expansion of the Universe and cosmic background radiation. Current models attempt to describe the future of the Universe as the processes that occurred in the first moments of the Big Bang are better understood.
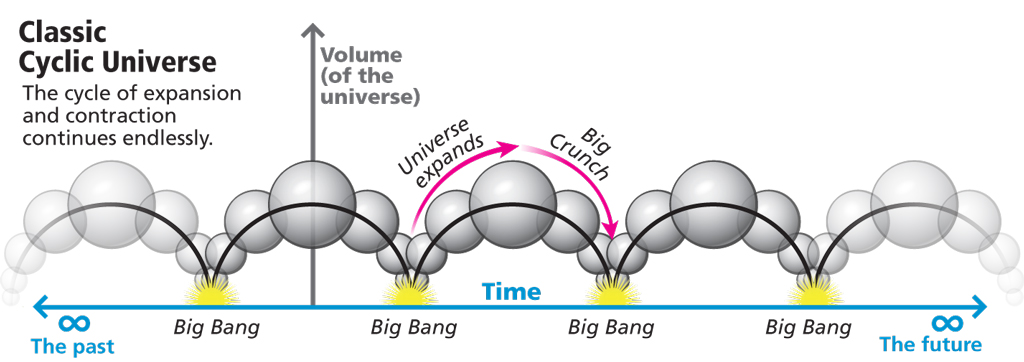
Pulsating Universe Theory
He says that the Universe did not actually have a common origin, but that it has been "creating" and "destroying" itself continuously, going through a phase of expansion and another of contraction (or "Big Crunch"), in a cyclical manner. It has lost popularity after works that demonstrate its scientific infeasibility, since it would require initial conditions that are not found according to the mathematical calculations of the primordial Universe, and do not allow us to conclude that before the Big Bang there was a previous Universe.
Steady State Theory
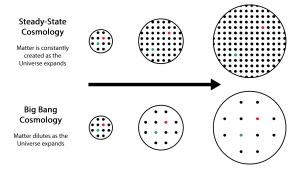
This theory, an alternative to the Big Bang, tells us that the density of matter in the expanding Universe remains unchanged, due to the continuous creation of matter, thus adjusting to the concept of "perfect cosmological principle", which states that the observable Universe is essentially the same at any time and place (homogeneous and isotropic in space and time), so it should look exactly the same anywhere (on large scales). Homogeneous is understood as any place in the Universe looks the same and has the same properties as any other place, while isotropy indicates that regardless of the direction in which one observes, the same properties of the Universe will be seen.
Although this theory had some popularity in the mid-20th century, dividing those who supported the Big Bang and the Steady State theory, it is currently rejected by the astronomical community, because observational evidence points to a cosmology originating in the Big Bang. and at a finite age of the Universe, incompatible with the stationary model.


