Due to the processes that occurred during the formation of the Solar System, a large amount of dust and debris particles were left wandering around, unable to join larger objects to form a massive object, such as a planet. Most of them are located in an area called Main Asteroid Belt, between Mars and Jupiter, while others are even further away, in an area beyond Neptune known as the Kuiper Asteroid Belt.
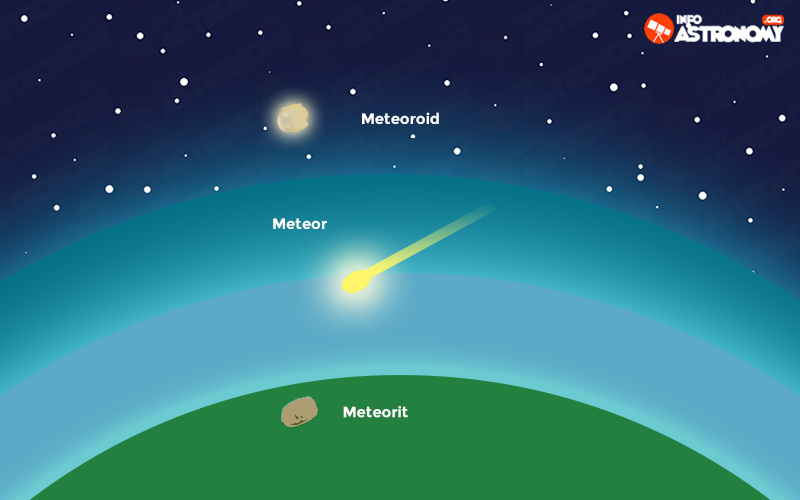
However, many of these particles (called meteoroids) do not have a defined location, and simply occupy an orbit that may be more or less close to the Sun. Or, as also happens, they correspond to particles that were left wandering after the passage of a comet around the Sun. So it happens that occasionally, when The Earth passes through an area of space that contains these particles, its gravity inevitably attracts them and the particles fall towards the planet. Because most of these loose particles are no larger than a grain of sand or rice, their passage through the Earth is very ephemeral.
The hot air pocket that forms around the particle, due to the high speed it carries, burns it after a few seconds and completely pulverizes it. This is what is commonly known as "Shooting Star", but whose real name is meteor. However, those debris that are somewhat larger have the possibility that a small part survives the fall, managing to reach the surface. In this case, the object fallen from space is called meteorite, and if we are lucky enough to find one, it can reveal important questions regarding the formation of the Solar System, since they are objects that have remained unchanged since then (about 4.6 billion years ago).

